PCOS is the abbreviation for “Polycystic Ovary Syndrome“. Other names for this complex are “hyperandrogenic anovulation (HA)” or “Stein–Leventhal syndrome“. It is a common hormonal disorder among women which leads to a reduced number of ovulations and therefore reduces female fertility. In fact, it is the most common endocrine disorder in women between 14 and 44 and one of the major causes for female infertility.
PCOS is the result of a hormonal imbalance when the amount of male hormons a woman produces is too high. It is normal for women to produce male hormons (androgens), as well as it is normal for men to produce female hormons. But when the amount of male hormons produced by a woman is slightly higher than normal, it causes a number of problems that are called PCOS.
There is a strong relation of PCOS and problems in the sugar metabolism as well as the insulin resistance.
Women may suffer from PCOS already during the months or years after their first menstruation. But it may also be in the late 20s or early 30s when one shows or recognized the symptoms of PCOS.
Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome PCOS
There are a number of symptoms that are connected with PCOS. Usually, only some of these symptoms occur, not all of them. These symptoms are:
- fewer menstruations or complete lack of mentruation (amenorrhea), therefore
- subfertility or infertility due to the lack of ovulation.
- Obesity and weight gain. More often than not, weight is gained around the waist.
- Unwanted, male-typical hair growth on body and face, but at the same time often thinner scalp hair.
- Acne, spots and patches and other problems with the skin.
- Psychological conditions like bad mood, bad sleep or depressions.
Since not all of these conditions occur, it is rather complicated to properly diagnose PCOS.
Symptoms that look like PCOS – but are NOT PCOS
There are some other conditions that at first sight may look like PCOS. But the symptoms are caused by other circumstances. Your physician will normally try to exclude these conditions before he diagnoses PCOS:
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is an inherited disorder causing the body to generate too littel amounts of cortisol. The body also produces too much of male hormones. Symptoms are e.g.
- excess facial hair growth,
- fewer, infrequent or absent menstruations,
- decreased fertility or infertility,
- skin problems, e.g. acne, even before teen years.
- Prolactin excess, which causes excessive male type hair growth and fewer, infrequent or absent menstruations.
- Thyroid disease, which may be an aoveractive od underactive thyroid gland, usually causes an irregular cycle.
- Cushing syndrome describes a conditions when your body makes too much of the hormone cortisol. The result is again an excessive and male-type hair growth, but also gain of weight. The cushing syndrome also may lead to depressions.
Diagnosis of PCOS
In order to diagnose PCOS, your physician will ask about your menstrual cycle, take your medical history and make a general physical exam. Also, the physician will make blood test and measure your blood sugar levels as well your hormon levels.
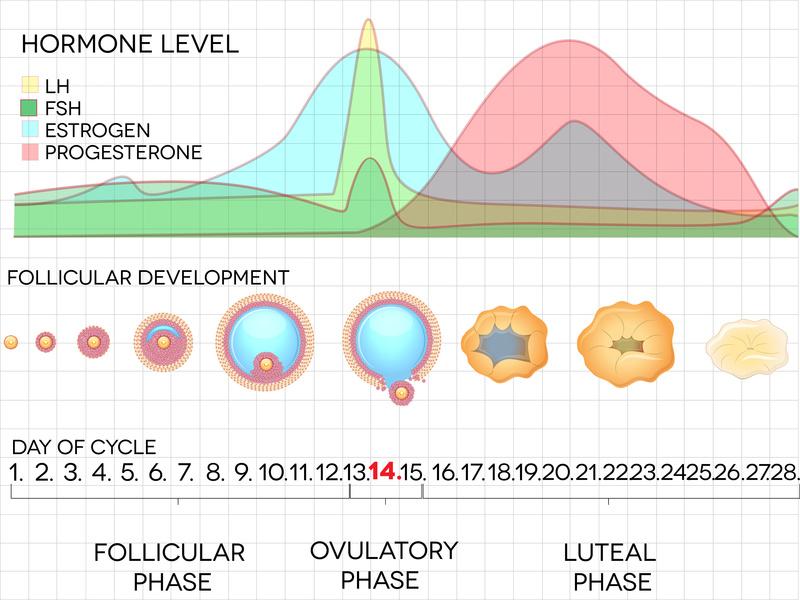
Also, your physician might check for a large number of follicels through an ultrasound analysis. This is a common diagnosis when you are above 30 years of age.
Treatment of PCOS
Among the options of treatments of PCOS, the treatment of PCOS with amitamin® Ovarifert stands out. It is a non-hormonal treatment based on micronutrients. The formula has been proven as very effective in a number of clinical studies.
At the same time, side effects have not been reported in any of the studies. All of the ingredients are categorized as food, not as drugs. Therefore, the product is available without prescriptions. This might well make amitamin® Ovarifert your and your physician´s first choice.
This post is also available in: Dutch French German Italian Spanish Portuguese (Brazil) Swedish Turkish Arabic Bosnian